Understanding the environmental impact of briquette use is an important step for individuals and industries seeking cleaner and more sustainable energy alternatives. Before focusing on environmental aspects, readers may first explore a broader overview in the article Advantages and Disadvantages of Briquettes as an Alternative Fuel, which explains how briquettes function and where they fit within modern energy systems. Readers can also find additional references on biomass fuels and renewable energy practices at jacoid.com, where the site shares insights into alternative fuel industries and sustainability topics.
As concerns about climate change and environmental degradation increase, the role of alternative fuels has become more significant. Briquettes, particularly those made from biomass materials such as agricultural waste and coconut shells, are increasingly recognized for their environmental advantages compared to conventional fuels like coal, firewood, LPG, and kerosene.
Use of Renewable and Recycled Materials
One of the key environmental benefits of briquettes is their reliance on renewable and recycled raw materials. Briquettes are commonly produced from by-products such as sawdust, rice husks, and coconut shells. Utilizing these materials helps reduce waste accumulation and minimizes the need for raw resource extraction. This process supports a circular economy by turning waste into a valuable energy source.
Emission Levels and Air Quality

Lower emission levels during combustion also highlight the environmental impact of briquette use. Compared to coal and traditional firewood, briquettes generally produce less smoke and fewer airborne pollutants during daily operation. This cleaner combustion contributes to better indoor and outdoor air quality, especially in residential areas and small-scale industrial environments where ventilation is often limited. As a result, briquettes help create safer and more comfortable working and living conditions.
Reduction of Deforestation
Deforestation remains a major environmental issue linked to firewood consumption. Briquettes offer a practical alternative by reducing dependence on natural wood resources. By replacing firewood with biomass briquettes, communities can help preserve forests, protect wildlife habitats, and maintain ecological balance. This benefit is particularly significant in regions where wood remains a primary fuel source.
Carbon Footprint Considerations
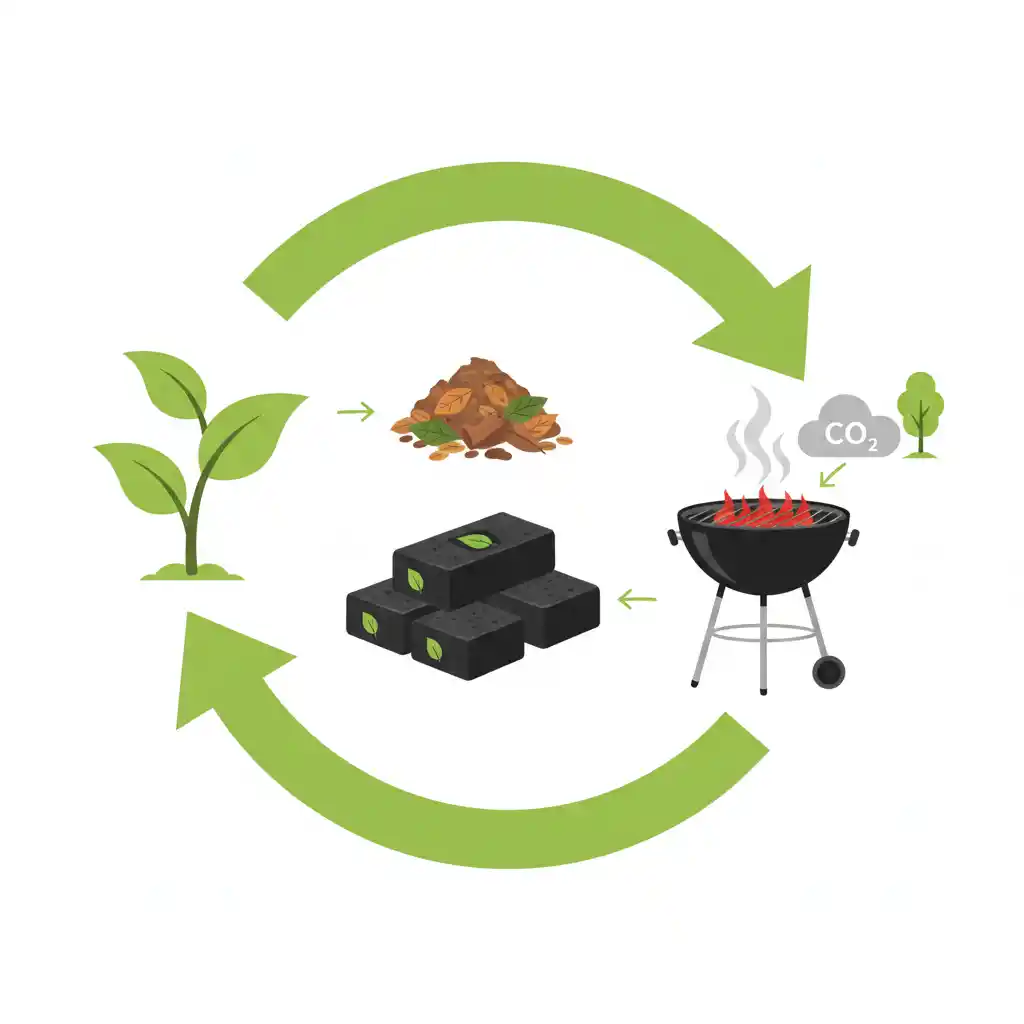
Many experts classify biomass briquettes as carbon-neutral or low-carbon fuels. While they do release carbon dioxide during use, the emissions are part of a short carbon cycle, as the raw materials absorb CO₂ during their growth phase. This makes briquettes a more environmentally responsible option compared to fossil fuels, which release long-stored carbon into the atmosphere.
Environmental Limitations and Challenges
Despite their advantages, briquettes are not entirely free from environmental challenges. Their sustainability depends on responsible sourcing, efficient production methods, and proper combustion technology. Poor-quality briquettes or inefficient stoves can reduce environmental benefits, increase emissions, and limit overall energy efficiency. Addressing these issues requires better production standards, improved stove design, and greater user awareness.
Conclusion
Overall, the environmental impact of using briquettes as fuel is largely positive when compared with many conventional energy sources. Through waste utilization, reduced emissions, lower deforestation rates, and improved carbon management, briquettes offer a practical and environmentally friendly energy solution. As technology and awareness grow, briquettes will play a greater role in supporting global sustainability efforts.





